
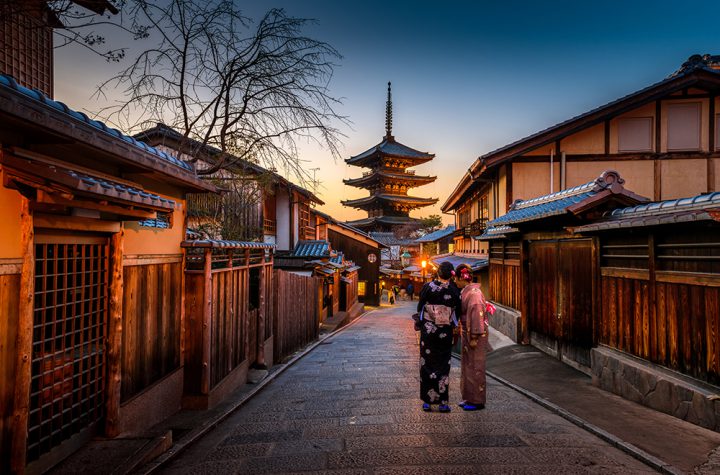
The unanimous ruling of the International Court of Justice (ICJ), on Thursday, on the prevention of alleged acts of genocide against Rohingya Muslims has finally pinned legal responsibility on Myanmars government for the militarys large-scale excesses of 2017. Crucial is the Hague courts stipulation that the civilian government of Ms. Suu Kyi submit an update, within four months, of the steps it has taken to preserve evidence of the systemic brutalities. Yangon has also been asked to furnish six-monthly reports thereafter, until the conclusion of the case, which relates to genocide accusations. The court has further emphasised that an estimated 600,000 Rohingya resident in Myanmar still remained highly vulnerable to attacks from the security forces. The ruling vindicates findings by the UN and human rights groups on the prevalence of hate speech, mass atrocities of rape and extra-judicial killings, and torching of villages in Myanmars Rakhine province, leading to the forced migration of thousands to Bangladesh. The ruling pertains to the Gambias suit on behalf of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC), alleging that the brutalities by the defence services amounted to crimes of genocide under the 1948 Genocide Convention. Arguing the defence in person during the three-day public hearings last month, Ms. Suu Kyi, who was elected in 2016, insisted that the 2017 violence was proportionate to the threat of insurgency. She even questioned the Gambias standing to bring the suit, saying that there was no bilateral dispute.
Rejecting the ICJs ruling, Myanmars Foreign Ministry has accused rights groups of presenting the Court with a distorted picture of the prevailing situation. In a statement, it defended the armys action as a legitimate response to violations of the law by the insurgent Arakan Rohingya Salvation Army. However, the above claim is at odds with the findings this week of an Independent Commission of Enquiry established by the government. The Commission acknowledged that war crimes had indeed been committed during the military campaign, when about 900 people were killed. But there was nothing to back the assertions of gang-rape, or evidence to presume any intent of genocide, it held. Although it could take years before the court pronounces the final verdict in the genocide case, Thursdays injunction is an important victory for the refugees languishing in Bangladeshi camps. It empowers the UN Security Council to prevail upon Myanmar to take appropriate measures for the rehabilitation and repatriation of displaced communities. As the biggest regional player, China could play a constructive role to ensure a speedy return to normalcy in its neighbourhood. India has its own interests in an amicable resolution of Myanmars internal dispute. Above all, finding closure to the current dispute would mark the completion of Myanmars return to civilian rule.




More Stories
The South Australian government has promised to deliver the “biggest hit of economic adrenalin in South Australian history” in Tuesday’s budget.
Boris Johnson will proceed with his controversial Brexit bill despite US president-elect Joe Biden having previously warned the UK over the draft legislation.
Singapore-based Nektar.ai, a productivity platform for sales teams, has raised $2.15 million in seed funding. Founded earlier this year, Nektar has been working in stealth mode with five companies, and has plans for an early adopter release before a public la…